In What Ways Is Paleolithic Cave Painting Like Our Modern Conception of Art?
Cave paintings and drawings were the outset uses of fine art in prehistoric times. Here we expect at the these artistic interpretations of the world byHomo sapiens.
Introduction to cave fine art
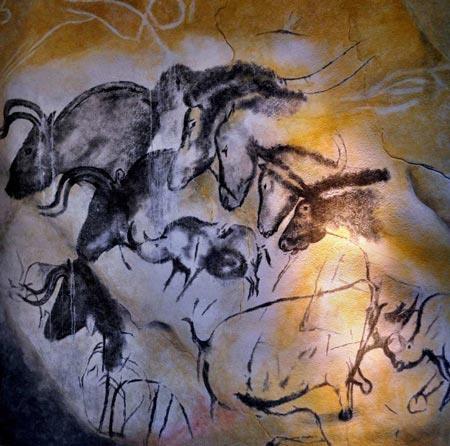

- Draw what you encounter.
- What practise you lot call up it was painted on?
- How onetime do you think information technology is?
- Why do you remember it was drawn and painted?
We call this cave art. It was painted on the walls of caves in Europe and in Asia during the Palaeolithic Menstruation some 325 million to 10,000 years ago. To get in easier to talk about events the period is broken upwardly into 3 periods.
The Palaeolithic period and humans
The first is the Lower Palaeolithic. It was dominated by a number of human-blazon people and later by the Neanderthals. And so around 300,000 years ago, we call this the Middle Palaeolithic followed by the Upper Palaeolithic (Table ane).
Table ane: Timeline of Palaeolithic Menses from 325 million to 10,000 years ago.
| Years ago | Period | People | Image of Culture |
| 3,500 30,000 | Upper Palaeolithic | Homo sapiens Cavern art with animals appears | © Giovanni Caselli |
| thirty,000 35,000 | Transition Middle to Upper Palaeolithic | Human sapiens spread across Europe Human neanderthalensis have disappeared | Courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech |
| 35,000 xl,000 200,000 300,000 | Middle Palaeolithic | Outset cave art Homo sapiens arrive in Europe Homo neanderthalensis announced in Europe | Christian Jegou Publiphoto Diffusion / Scientific discipline Photograph Library |
| 300,000 1.6 million i.ix 1000000 2.3 one thousand thousand iii.iv million | Lower Palaeolithic | Hand axes announced Homo erectus (Africa) Human being habilus (Africa) | By T. Goskar and Thousand. Nichols, copyright Wessex Archaeology |
The Upper Palaeolithic Period is very different from the Middle and Lower periods. People look different and the civilization (ideas, customs, and social behaviour) of the people are different. Over the unlike periods humans were generally hunter-gathers who used tools and fire, and from the Lower period onwards they seem to have buried their expressionless.
Differences between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens
Information technology would exist incorrect to try and explain the success of Human sapiens in the Upper Palaeolithic by thinking that they were more intelligent than the Neanderthals (Man neanderthalensis) of the Lower and Center Periods.
Maybe it was the development of language, since it is clear from the evidence that Neanderthals were tool-makers and lived in groups. It's not clear if they had a language but their brains were approximately the same size as Human being sapiens.
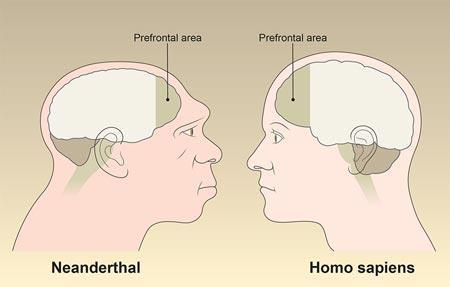
Studies of the brains capacity and structure imprint on the skull to determine brain organization by Dunbar and Pearce (2013 Scientific discipline Daily) have suggested that it is possible Neanderthals could have produced other things besides tools. In fact Neanderthals brain evolution indicates an increased development in the sensory especially vision and motor centres, primarily in the rear one-half of the brain. Human being sapiens show a dissimilar type of development, primarily in the frontal lobes. These are the higher thinking centres of the brain, and indicate a development in speech, imagination, and ideals centres.
Evidence of early on art
It is clear that 1 divergence is that the Upper Palaeolithic people produced circuitous advice and fine art. Fifty-fifty in this area though there needs to be intendance, and the complexity of this research area can be illustrated by the Makapansgat cobble from South Africa.
This cobble is a reddish jasper (silicate mineral containing atomic number 26 oxide) rock which appears to have the shape of a head. Information technology seems to accept been carved with distinctive 'staring eyes' and a 'mouth'. Firstly nosotros know that jasper could non have occurred naturally in the dolomite cave where it was found, so it must have been carried there.
Secondly, the markings do not appear to be natural they acquit all the impressions of having been carved.

Thirdly, because of the place it was found in and the materials effectually it, it has been suggested that it was deposited in the cave past Australopithecus africanus. They were dominant in the Lower Palaeolithic Period most three meg years ago. [i] That is a long fourth dimension before Homo neanderthalensis allow lonely Homo sapiens.
Bednarik who studied this cobble claims that, quondam effectually 850,000 years ago, the people of the Lower Palaeolithic were engaged in behaviour which could exist interpreted as 'fine art'. Testify shows they decorated themselves with beads, collected exotic stones and there is prove of the collection and utilise of ochre every bit a decoration.
- Is this show of a spiritual development?
More substantial bear witness of this spiritual character, that could have led to cavern art, is burials from the Lower Palaeolithic period about 350,000 years agone. These burials comprise grave goods and the people used colour on their bodies in the form of tattoos.
These tattoos are drawn using such minerals equally ochre, manganese oxide or charcoal. Later they painted on cave walls using lines, circles and Five markings. It is later in the Upper Palaeolithic period that there is the appearance of carved anthropomorphic (animal and man) images with strange symbols and marks and the creation of cavern paintings.
All this evidence would suggest Palaeolithic humans had begun to believe in supernatural or spiritual beings early. [two] Indeed, Lewis-Williams [iii] argues this behaviour has its evolutionary origins in Africa as a gene of human consciousness.
The Importance of cave art and homo evolution
It tin can be argued that we have e'er collected things and doodled, so how is that connected to the cave paintings?
Archaeologists argue that collecting is connected to ritual (a serial of deportment performed co-ordinate to a prescribed social club) and that is an indicator of a belief system or religious behaviour. So ritual and faith is an essential mark of modern human behaviour. It has been said that information technology displays the emergence of the modern listen.
From the evidence available it is assumed that this attribute of man behaviour emerged around 40 - 50,000 years agone. If that is true, information technology's the transition from the Middle to Upper Palaeolithic period and the advent of the modern homo.
Cavern painting is considered 1 of the first expressions of the human animal's appreciation of beauty and a representation of a mystic or sacred side to life. Hundreds of images of animals in vibrant colour and striking poses of action tin be seen in the prehistoric art gallery on rocks worldwide. There are many examples in France and Kingdom of spain.
These cave wall paintings are known every bit pictographs and are found all over the world aslope petroglyphs (the incised, pecked or cut designs on rock surfaces).
Cavern drawings are they art?
Weren't they used for education young hunters?
The give-and-take fine art does not announced before the 15th century so the Palaeolithic people did non know it as art. Using the discussion art from the 15th century means that the Egyptians, Greeks and Romans had no word for art.
In fact art is a Middle English word coming from the Latin ars (skill or technique). The first utilize of the word fine art was when it was used to show a marker of human accomplishment in the early universities and that exists today in the Available of Arts (BA) or Main of Art (MA) awarded by universities.
Withal, fine art is more than a skill or technique. It has a purpose going beyond making something. Any connection with our modern utilize of the give-and-take fine art did non appear until the late 1600s.
Then it is possible some of the pictures were used to teach immature hunters just and then many of them have other characteristics that mean there had to have been links with some belief organization.
Were all the cavern paintings of animals?
No, in El Castillo cave, Northern Spain, at that place are Palaeolithic paintings. These are stencils of hands and disks made by blowing paint onto the wall and date back at least 40,800 years'. This makes them Europe's oldest known cave art.[iv] In France the cavern paintings of Chauvet take been dated to 33,000 years ago; the paintings plant at Lascaux to 17,000 years ago; and those at Niaux between fourteen,500 and thirteen,500 years agone. Each set of paintings bear witness differences and a development in style of representation.
In Chauvet the drawings depict animals. It is suggested that these stand for the animals that provided the people with food and raw materials along with the predators that endangered or competed with them. The Lascaux paintings, on the other mitt, show depictions of foreign beasts such every bit ones that are one-half-human and half-bird and others that are one-half-human and half-lion. Those in Niaux are depicted as a huge frieze showing bison, deer, ibex, and horse and there are carvings showing salmon or trout and bears claws.[v]
Consequently, some archaeologists have seen these representations as indications of the development of a grade of organized religion. The paintings in Niaux were made as the Last Glacial Maximum began to warm and seem to be an impression of the animals effectually the people, indicating a spiritual expression of existence.



Distribution of cavern drawings
In that location are very different drawings in each cavern, only were paintings the merely things the people produced and were French republic and Spain the only places?
The distribution of cavern fine art is worldwide but in Eurasia it is nearly abundant in areas that are also rich in decorated objects including:
- the Périgord, the French Pyrenees, and Cantabrian Spain;
- Portugal, where there are Palaeolithic decorated caves;
- the very south of Espana to the northward of French republic;
- southwest Germany, where traces have been found;
- Italy and Sicily, which accept some concentrations;
- Slovenia, Romania, Bulgaria and Russian federation.
The current total for Eurasia is about 280 sites. Some like Creswell Crags, England, comprise only one or a few figures on the walls, others like Lascaux or Les Trois Frères have hundreds.
The following map shows the limits of the Last Glacial Maximum. It likewise shows the main sites of cave art in Eurasia and though not fully inclusive of all cavern art it is a good indicator of the spread.
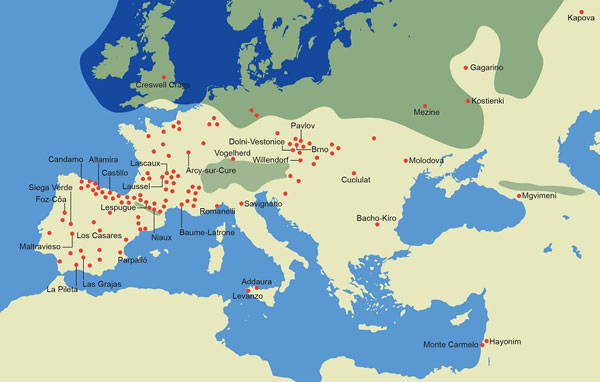
Distribution of primary Palaeolithic cave-art locations in Eurasia. Peter Balderdash.
It's interesting to note that and so many cave fine art sites are found in groups while some are just single sites. Nevertheless, it would be unfair to draw too many conclusions from this map since there are and so many factors affecting the presence of cave paintings. The most of import is the climate of the surface area. So, every bit only a few take been found in the temperate wet climate of United kingdom, and so does that mean the people in the British Isles drew petty cavern art or has the bulk been eroded abroad?
A striking feature of many of these cavern paintings is the fact that they are frequently in large caverns with interesting sound qualities.
- So, was singing or chanting some other aspect of the art experience for the Palaeolithic peoples?
The evidence would be the existence of musical instruments, and flutes from 42 - xl,000 years ago made from bird bone take been found and reconstructed. They evidence the people had an understanding of how length, diameter and position of holes influenced the audio.v Did they play just 1 instrument at a fourth dimension or did they play in groups? We tin only wonder at the sound these people produced.
Source: https://edu.rsc.org/resources/cave-art-history/1528.article




0 Response to "In What Ways Is Paleolithic Cave Painting Like Our Modern Conception of Art?"
Post a Comment